Shared line across sites#
Overview#
The ability to have shared lines across sites allows lines to be shared across sites, and is accomplished by introducing the concept of an “inventory site”, in addition to “real sites”:
The inventory site is used to provision the shared lines first
Then the real sites make use of the shared lines by assigning them to phones
Devices are only provisioned on real sites (not in the inventory site).
The “shared lines** feature also supports hunt groups and call pickup groups across sites by leveraging the inventory site to provision all of the lines to be included in the hunt group or call pickup group.
Lines used in the hunt groups and call pickup groups that are provisioned in the inventory site can span multiple real sites; that is, they’re used by devices on the real sites. The key requirement is that all the lines to be used by a given hunt group or call pickup group must be configured in the inventory site, along with the hunt group and call pickup group itself.
The “shared line across sites” deployment model is 100% backward compatible with the previous directory number (DN) and line configuration. Existing deployments are not impacted when the system is upgraded, and all existing dial plan configuration procedures are supported. The deployment configuration shown in Example of shared line across sites is optional and is only required when sharing lines across sites.
Tip
If a line is potentially shareable, it is recommended that you create the line in the inventory site, even if it won’t be shared across sites immediately.
The system does not support the ability to move a line from a real site to an inventory site, so to convert a line from site-local to cross-site shared, the line would need to be deleted from the real site and recreated in the inventory site.
Note
See the Glossary for descriptions of the following terms related to shared lines across sites functionality:
Directory Number (DN)
DN Inventory
E.164 Number
E.164 Inventory
Line / Line Relation
Line Appearance
Class of Service (CoS)
Directory Number Routing (DNR)
E.164 Associations
Limitations of shared lines across sites#
When considering using shared lines across sites, consider the following limitations:
A new inventory site is required for each new combination of network device list (NDL) and Country (a “site group”); that is, lines configured at the inventory site are specific to the NDL and Country defined for that site.
All real sites that reference lines in an inventory site must be defined with the same NDL and Country. Ensure that this requirement is met, as it is not enforced in Automate.
Shared lines can’t span countries or NDLs. This is necessary because Cisco UCM doesn’t support shared lines across clusters. The country must be consistent so that line CoSs (defined in the inventory site) are correct for each device referencing the line (defined in the real site). Ensure that the correct association is made between inventory sites and real sites, as it is not enforced in Automate.
When configuring a phone or user at a real site, any reference to a DN that does not exist in the inventory site results in a new line being created at the real site as it did prior to this Cisco HCS release. If the inventory site doesn’t exist, or a line hasn’t been configured in the inventory site first, the system behaves as it did in previous Cisco HCS releases (backwards compatible).
If a line can be potentially shared, create it in the inventory site before referencing it by any devices. If the DN is used in a device before it’s configured in the inventory site, the line is created in the real site and may not have the desired CoS or other configuration desired for a shared line.
When a line has been created (either at the inventory site or a real site), it can’t be moved. To move the line, delete it and re-add it. For example, if you forget to define the line at the inventory site first and configure a device with a line, the line is created at the real site. You would need to delete the line from the real site and add it to the inventory site, then reassign it to the phone.
A site admin logged in to a real site is not able to see the line configuration that exists at the inventory site. A custom admin (or above) can view the line configuration at all of the sites.
The “shared lines across sites** functionality only works when using a flat dial plan since other dial plans have site location codes in the DN that won’t make sense if the DN is shared by multiple sites. The default Automate template bundle includes a Type 4 flat dial plan. Other, non-site-specific custom dial plans can be used.
Self-provisioning does not work for DNs defined at the customer level.
Although an admin can delete inventory sites, this is not recommended. If an inventory site is deleted, all hunt groups, call pickup groups, voicemail pilot associations, and lines that are part of the inventory site are deleted. If there are devices on the “real” sites that reference these lines, they will no longer reference these lines as they will have been deleted. The customer-level DN inventory is still intact, though no lines are associated with these DNs because they are deleted when the inventory site is deleted. The hunt groups and call pickup groups are self-contained to the inventory site and are therefore deleted as part of the deletion of the inventory site.
When the inventory site is deleted, this deletes all shared lines, Classes of Service, DNR, and any other configuration added at that site. The shared lines are removed from all devices on “real” sites that may have referenced them.
If an emergency number is dialed from any shared line, the number displayed on the other end should be the Emergency Call Back Number of the corresponding site.
Example of shared line across sites#
Phones are always configured on real sites, and can use both shared and site-local lines. For example, each phone can have one site-local line (for example, 1000), and one cross-site shared line (for example, 9000). The following is a summary of the configuration that resides at each hierarchy type:
Customer hierarchy
DN inventory - for the lines to be shared across sites.
Note
The DN inventory is visible across all sites under the customer. Allowing DN Inventory to be configured at the customer hierarchy node is an enhancement for the Shared Line Across Sites feature. Note that DN inventory can only be created at the customer hierarchy node when a non-SLC-based customer dial plan has been deployed. A transaction error is sent if the administrator attempts to create customer level DN inventory with an SLC-based dial plan.
Inventory site, includes:
Line relations - for the DNs to be shared across sites.
Directory Number Routing (DNR) entry for the line relations configured at this site to make the DNs inter/intra-site dialable.
E.164 inventory - for the line relations configured at this site.
E.164 associations - for the line relations configured at this site.
Line Class of Service (CoS) - for the lines configured at this site. CoS is discussed in more detail in Class of service for shared line across sites.
Short codes - for the line relations configured at this site.
Real site, includes
DN inventory - for lines to be used only at this site. Note that these DNs can be shared by multiple phones within the site.
Users - configured via Users page or Quick Add User.
Line relations - for the DNs configured at this site. These line relations do not have to be configured first; they are configured automatically any time a phone, extension mobility profile, or remote destination profile references a line that doesn’t exist in the inventory site.
Directory Number Routing (DNR) - for each of the line relations configured at this site.
E.164 inventory - for lines created at this site.
E.164 associations - for lines created at this site.
Device Class of Service (CoS) - to be used for the phones configured at this site.
Phones - these phones can reference lines that were defined in the inventory site or the Real Site where the phone exists.
Extension mobility - these profiles can also reference lines that were defined in the inventory site or the Real Site where the phone exists.
Single Number Reach - these profiles can reference lines that were defined in the inventory site or the Real Site where the profile is defined.
Fields in Automate that reference DNs, such as the Pattern field in the Line tab of a phone, are in a drop-down list of DN inventory. The drop-down list of DNs includes inventory defined at the customer level, combined with the inventory defined at the current site context. The administrator can chose either a cross-site shared DN or a site-local DN.
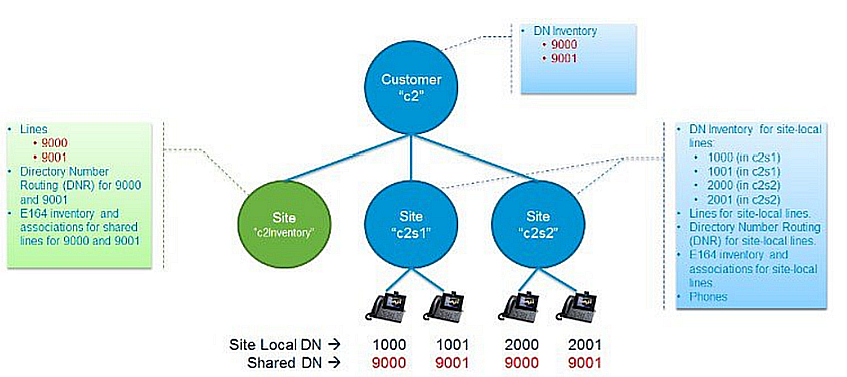
Diagram showing shared line across sites configuration
The image provides a basic shared line across sites configuration:
Uses one inventory site (“c2Inventory”) and two real sites (“c2s1” and “c2s2”)
Shows two shared DNs (9000 and 9001 shown in red) and four site-specific DNs (1000 and 1001 at c2s1, 2000 and 2001 at c2s2).
The inventory for the shared DNs are provisioned at the customer hierarchy to make them visible to all sites under the customer. This allows the sites to configure the associated line and assign the line to a device.
The inventory for the non-shared-across-sites DNs is still configured at the real sites (in blue) as it was in previous Cisco HCS releases.
Note that both shared DNs and non-shared DNs can co-exist for the same customer.
Configure shared line across sites#
The steps for configuring shared lines across sites is generally the same as with conventional lines. This section highlights the differences.
Conventional, site-local lines: Lines can be configured automatically as part of the phone, user, or Quick User workflows. Lines don’t need to be configured separately first
Lines to be shared across sites: Lines must be configured first in the inventory site, then referenced from phone, user, or Quick User workflows.
Configure shared line across sites at customer#
The customer configuration is similar except that you create DN inventory at the customer hierarchy for lines you would like to share (or potentially share) across sites.
Configure the Cisco UCM and Cisco Unity Connection (CUC) devices. These can be at the customer level (dedicated) or above (shared).
Configure the customer normally (for example, c2).
Configure the Network Device List (NDL) for the customer (for example, c2Ndl) that will be used for your site group (NDL/Country combination).
Deploy the customer dial plan.
This must be a flat dial plan (for example, Type 4) since shared lines across site dictates that DNs cannot be site-specific. The Type 4 dial plan does not impose site-specific structure (in other words, site location codes). When configuring the customer dial plan, ensure that the Site Location Code check box is unchecked.
Configure the DN inventory to be used across sites for shared lines (via the Directory Number Inventory). Note that you should leave the site drop-down list empty to create the inventory on the Customer hierarchy node.
Configure shared line across sites at inventory site#
The inventory site is only needed if you want to configure shared lines across sites. If you do not have this requirement you do not need an inventory site and configuration is exactly as it is done normally. Most of the inventory site configuration is the same as configuration for a real site (for example, deploy site dial plan, configure DN inventory, and so on). The areas that are unique to the inventory site are provided in Steps 1, 3, and 5.
Configure the inventory site and specify the NDL and Country, for example, c2InventorySite. A different inventory site is needed for each NDL/Country combination (site group). If the customer only has one NDL and one Country, they only need one inventory site.
Deploy the site dial plan (Type 4 will automatically be used based on the customer dial plan that was deployed).
Create the new Classes of Service to be used as the default line CSS and update the Site Defaults procedure for the inventory site.
Configure Directory Number Routing (DNR) for the shared lines (via Directory Number Routing).
Create line relations for each shared line (via Line).
Create E.164 inventory (via Add E164 Inventory).
Associate E.164 to DN (via E164 Associations (N to N)).
Configure Hunt Groups that use shared lines (via Hunt Groups).
Configure Call Pickup Groups that use shared lines (via Call Pickup Groups).
Configure shared line across sites at real sites#
Configuration at the real sites is almost exactly the same as in past Cisco HCS releases. The major difference is that the Shared Lines Across Sites exist at the inventory site and therefore any configuration associated with those lines (CoS, DNR, E.164 associations, and so on) exists at the inventory site.
Configure the real site (for example c2s1, c2s2, and so on). Use the same NDL and Country as the inventory site (same site group).
Deploy the site dial plan on each of the real sites (again, the customer dial plan enforces that the flat dial plan is used).
Create DN inventory for an DNs that will be used only at this site.
Create Directory Number Routing (DNR) for any DNs created at this site.
Create E.164 inventory and associations for an DNs created at this site.
Create Device Class of Service if needed. See Class of service for shared line across sites.
Create Line Class of Service if needed for your site-specific lines. Refer to Class of service for shared line across sites.
Configure users and phones (via Quick Add User, or Phones).
When configuring normal lines (lines that aren’t shared across sites), select a line from the local site DN inventory, not the customer-level DN inventory. The line is created at the local site as normal; you can configure line CoS, DNR, E.164 associations at this site as normal. Note that this includes shared lines that are only shared within the site.
When configuring a shared line across sites, select a customer-level DN from the drop-down list. Remember, the line should be configured at the inventory site first.
Configure site-specific Hunt Groups that use lines local to the real site.
Configure site-specific Call Pickup Groups that use lines local to the real site.
Dial plan type for shared line across sites#
The shared lines across sites functionality only works if you’re using a flat dial plan (Type 4), or a custom, non-site-specific, dial plan. This is because other dial plans (Types 1 to 3) have site location codes in the DN that don’t work if the DN is shared by multiple sites.
If you’re using predefined dial plans, ensure the Site Location Code checkbox is clear (disabled) when deploying the customer dial plan.
Class of service for shared line across sites#
Class of Service (CoS) refers to a Calling Search Space (CSS) that is specifically used to define call routing and feature processing for a line or a phone.
Several CSSs are defined when a customer and site dial plan are deployed. Some of these are only used internally (don’t select these CSSs in the CSS drop-downs when configuring a line or phone).
Class of Service CSSs are listed on the Class of Service page. A few example CoSs are predefined when a site dial plan is deployed, but the intent is for the administrator to create their own CoSs to meet the desired call routing and feature processing behavior. Below is a summary of Class of Service as it pertains to Shared Lines Across Sites feature.
Class of service is used in two places in Automate:
Line calling search space (via the Lines page, Directory Number Basic Information tab, Calling Search Space)
Device calling search space (via User Management GUIs, Phones page or Users page, Calling Search Space Name setting)
Additionally, CoS can provide line-based routing (LBR) or device-based routing (DBR). For each call made from a phone, the device CSS of the phone is combined with the line CSS of the line from which the call is being made, and the features and routing for the call are processed based on the combined list of partitions of these two CSSs. The default set of CoSs provided when a site dial plan is deployed includes a device CoS for emergency dialing only, and several line CoSs for feature processing, national dialing, and international dialing and that support either DBR and LBR. The following table shows the default allocation of feature and routing duties between the two sets of CoSs.
Feature |
Default Device CoS |
Default Line CoS |
|---|---|---|
Emergency call routing |
yes* |
- |
Intrasite routing |
- |
yes |
Intersite routing |
- |
yes |
Local PSTN call routing |
- |
yes** |
National PSTN call routing |
- |
yes |
International PSTN call routing |
- |
yes |
Feature processing |
- |
yes |
Table: Default Class of Service for Shared Line Across Sites Feature
* Emergency call routing is dependent on the country configured for the site. The country is used to route to the correct emergency number for that country (for example, 911 routes to 112 in the United Kingdom). Emergency call routing is assigned to the Device CoS because it is location-dependent, and must be tied to the site where the phone/user actually resides.
** Local call routing is dependent on local area codes defined in the site dial plan. The local area codes configured in the site dial plan allow dialing local dialing (for example 7-digit dialing in the United States).
As shown in the table above, routing is weighted heavily toward the line CoS because when the CoS is assigned to the line, it applies equally to the phone, extension mobility, and single number reach, which all typically share the same line configuration and provide similar dialing behavior for a given user. However, this assumes that the lines and devices are all constrained to individual sites. When we open up lines to be shared across sites, the site-specific configuration becomes more important in order to determine what to put in the device CoS versus the line CoS.
Class of Service (CoS) management for Shared Lines Across Sites is heavily dependent on the customer’s specific deployment scenario. The distribution of work between the device CoS and the line CoS depends on the type of country dial plan, and the dialing behavior the customer wants.
For example, if the country dial plan is flat and closed like the Swiss dial plan, meaning that the user numbers are not variable length and there is no site-specific area codes (only national dialing), then most of the routing can occur in the line CoS because there is not much site-specific dialing behavior.
However, if the country dial plan uses area codes and the customer wants a local dialing experience (ability to dial a shorter number such as 7-digit dialing in the United States, and relying on the dial plan to fill in the local area code), then local call routing must be in the device CoS because the device context is needed to determine which area codes to apply to the dialed number. Feature processing partitions can almost always stay with the line CoS since there is usually no geographic dependencies for the feature processing. The exception to this is Time of Day (TOD) routing which may vary depending on the site.
The table provides details for determining how to distribute routing and feature processing between the line CoS and device CoS.
Feature |
Line CoS |
Device CoS |
|---|---|---|
Emergency call routing |
- |
Emergency routing should always be location-specific |
Intrasite routing |
Always using the PrelSR route partition |
- |
Intersite routing |
Always using the PrelSR route partition |
- |
Local call routing |
When full E.164 number is always dialed for offnet calls, for example, national dial plans with no local call routing |
When site-specific area codes and/or variable length user numbers (local dialing behavior) are defined |
National call routing |
If local dialing is line-specific, national dialing should be line-specific. |
If local dialing is device-specific, national dialing should be device-specific. |
Toll-free call routing |
If local dialing is line-specific, toll-free dialing should be line-specific. |
If local dialing is device-specific, toll-free dialing should be device-specific. |
International call routing |
If local dialing is line-specific, international dialing should be line-specific. |
If local dialing is device-specific, international dialing should be device-specific. |
Service call routing |
If local dialing is line-specific, service number dialing should be line-specific. |
If local dialing is device-specific, service number dialing should be device-specific. |
To speed up the process of configuring lines and phones when you create new Classes of Service, set the site-specific default line CSS and site-specific default device CSS (Site Management > Defaults). These fields appear in the following tabs:
Device Defaults > Default CUCM Device CSS
Line Defaults > Default CUCM Line CSS
Call forward considerations for shared line across sites#
As the administrator, you can create the Call Forward CSS as a CoS for a particular deployment scenario. Considerations must be made based on whether the local, national, and/or international dialing is configured on the device CoS or line CoS.
Be aware that if the Call Forward CSS allows national and local PSTN routing, you may need to consider call forward scenarios when a line is not associated to a device and PSTN dialing is in the device CoS.
Phone, user, and Quick User for shared line across sites#
Phones and users should only be created at real sites and not at inventory sites. However, the system workflows don’t enforce this rule, but will help facilitate ongoing management of the configuration data for the customer.
Lines referenced in the Phone screen, the Users screen, or the Quick Users screen are created automatically if they have not already been provisioned in the inventory sites and pushed to Cisco UCM. This is acceptable as long as you intend for these lines to be only referenced within one site. If a line gets created on a real site that you intended to share across sites, it is recommended that you delete the line, and recreate it in the inventory site.
Relevant fields for shared lines across sites on the Phone screen are:
Phone tab: On this tab you specify the Calling Search Space Name (that is, the device-based routing CoS, which is by default the emergency routing CSS). Depending on choices made above in the Class of Service section, you might chose a different CSS here.
Lines tab: On this tab you select the DN (Pattern) from the drop-down list, and configure the E.164Mask used for line presentation. The DN drop-down includes DNs from the Customer DN inventory combined with the current site DN inventory.
At the time of writing, the E.164Mask is a free-form field and is not tied to the E.164 inventory; it must be manually entered.
The Route Partition Name field is automatically populated with the correct directory number partition based on the Pattern (DN) chosen. Similar fields exist in the User tabs.
Hunt groups and call pickup groups for shared line across sites#
Hunt groups and call pickup groups can be set up in either the inventory site or in the real sites, with the following conditions:
Inventory site: When configured in the inventory site, the hunt groups and call pickup groups can include any line created in that site, but not from other sites.
The recommended setup is to use the inventory site if your hunt group or call pickup group needs to include lines from multiple sites.
The real sites. When configured in the real site, the hunt groups and call pickup groups can include lines from the real site, but not from other sites.
Example scenario
The image provides an example of a hunt group that uses lines spanning multiple sites.
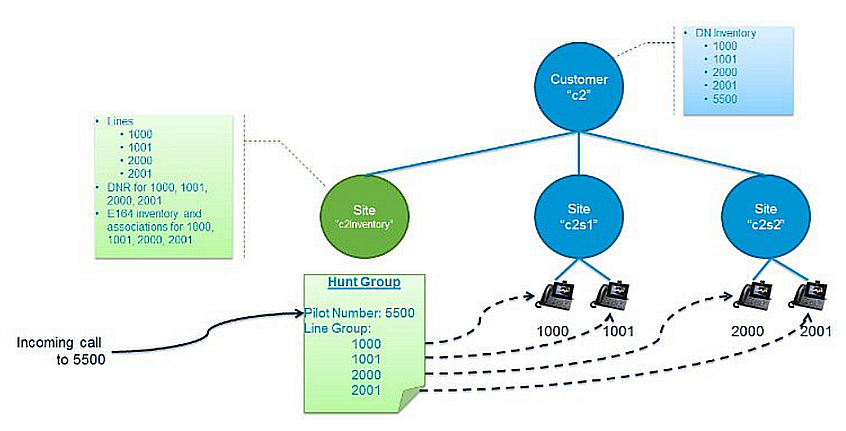
In this example, the hunt group includes the following lines:
1000
1001
2000
2001
These lines are not shared across sites, but to include them all in one hunt group, they must all be configured at the inventory site so that they can all be grouped under a single hunt pilot number, 5500.
Note
The hunt pilot directory number (DN) inventory is at the customer level.
Once the hunt pilot is assigned, that DN becomes unavailable for other uses:
It can’t be assigned to a device as a line
It can’t be used for another service pilot number
Handling voicemail to secondary shared lines#
To handle voicemail to secondary shared lines, create a separate user for each shared line at the Inventory Site level, then enable the voice mailbox for that user so that it can be managed by all shared lines.
This approach:
Offers the ability to differentiate between voice mail deposited for primary and secondary lines
Provides separate message waiting indication (MWI) notifications for voice mail in the phone’s primary and secondary line
Allows all configuration to be done in Automate. There are no separate manual configurations required in Cisco Unity Connection (CUC) or Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM).
Note
One additional license is required for the shared line user mailbox.
