Authorized Admin Hierarchy Roles#
Overview#
The Authorized Admin Hierarchy Roles feature in Automate addresses two general use-cases in administrator management (a combination of these solutions can also be applied).
For an administrator who needs a single user account configured as both an end user (with services) and an administrator.
This supports the following:
A single set of credentials for administration and end user access
Simplified external authentication (LDAP and SSO)
Support for concurrent use of both admin and self-service portals in same browser
For further details, see: End User and Administrator details.
For an administrator who needs to manage administrative domains outside of a single hierarchy, access to a matching subset of hierarchies can be configured, for example, for a customer administrator who administers only a subset of sites in customer hierarchies (one or more), the feature allows access to the matching subset of sites.
This restricted access applies to any hierarchy-related activities and items - tasks and elements that rely on or reside at a specific hierarchy.
Note
If a hierarchy is authorized, the authorization also applies to any child hierarchy nodes of this hierarchy.
The
LinkedSitehierarchy node type is included in theSitenode type authorization.An administrator who is configured as both an end-user and administrator can therefore also be an administrator who has been set up with an authorized admin hierarchy role.
Some functionality in Automate requires access to all lower hierarchies, so that an authorized admin hierarchy role needs be configured accordingly to use the feature. For example, for the Overbuild feature, the administrator must have permissions to the customer “From” hierarchy, which implies access to all sites under the customer. On the default dashboard and menu items providing access to the Overbuild feature, a macro condition with a hierarchy node type set to
Customerneeds to evaluate totruebefore the items are accessible:For details on the macro, see: Hierarchy functions(( fn.authorized_admin_allowed_hierarchy_level Customer == fn.true ))
The following areas are for example impacted by the subset of hierarchies:
List views reflecting items at a hierarchy
Drop-down lists on a form that are related to hierarchy elements
Filtered views and lists
Tree views showing a hierarchy exposed to the administrator
Items within hierarchy trees but outside of the allowed subset of hierarchies will not be available to be managed and are only be shown to indicate where allowed hierarchy elements reside in the hierarchy tree. For example, if sites from multiple customer hierarchies are allowed, then the display of these sites in the hierarchy tree may require showing the parent customer node, but the customer hierarchy will not be available for management.
Dashboard data displayed in widgets - obtained from resources that reference data at allowed hierarchies
Transactions and transaction views
Search results
When a global search is performed, the results that are returned are filtered by the administrator’s allowed hierarchies.
Workflows and actions carried out by the system API involving macro queries
Management activities on items at a hierarchy (Modify, Add, Create, Delete). This includes bulk load activities.
Important
Where this feature is used by an administrator, the administration tasks and concepts described in the documentation should be read and understood in accordance with the restricted access that applies to such an administrator.
The selection of hierarchies for authorized admin hierarchy roles is carried out by means of transfer boxes. This feature supports a maximum of 500 entries, so that a Selected list can be up to 500 hierarchy entries. Customers wishing to select more hierarchies must contact VOSS through their account manager or support. Significant performance degradation might be experienced with more than 500 entries.
For further details, see: Administrator access to a subset of a hierarchy details.
Manage Authorized Admin Hierarchy Roles#
Note
If the authorized admin hierarchy role is to be applied to an administration user,
this hierarchy needs to be the same or above the hierarchy as the user (data/User).
To create an instance of an authorized admin hierarchy role at the relevant hierarchy level:
Log in and go to the Authorized Admin Hierarchy Roles page.
To add or modify an Authorized Admin Hierarchy Roles instance, either add or modify the instance Name and select the Role.
Available roles will also include those roles containing the current hierarchy where the created Authorized Admin Hierarchy instance resides, in their Hierarchies Allowed list - see: Role Management.
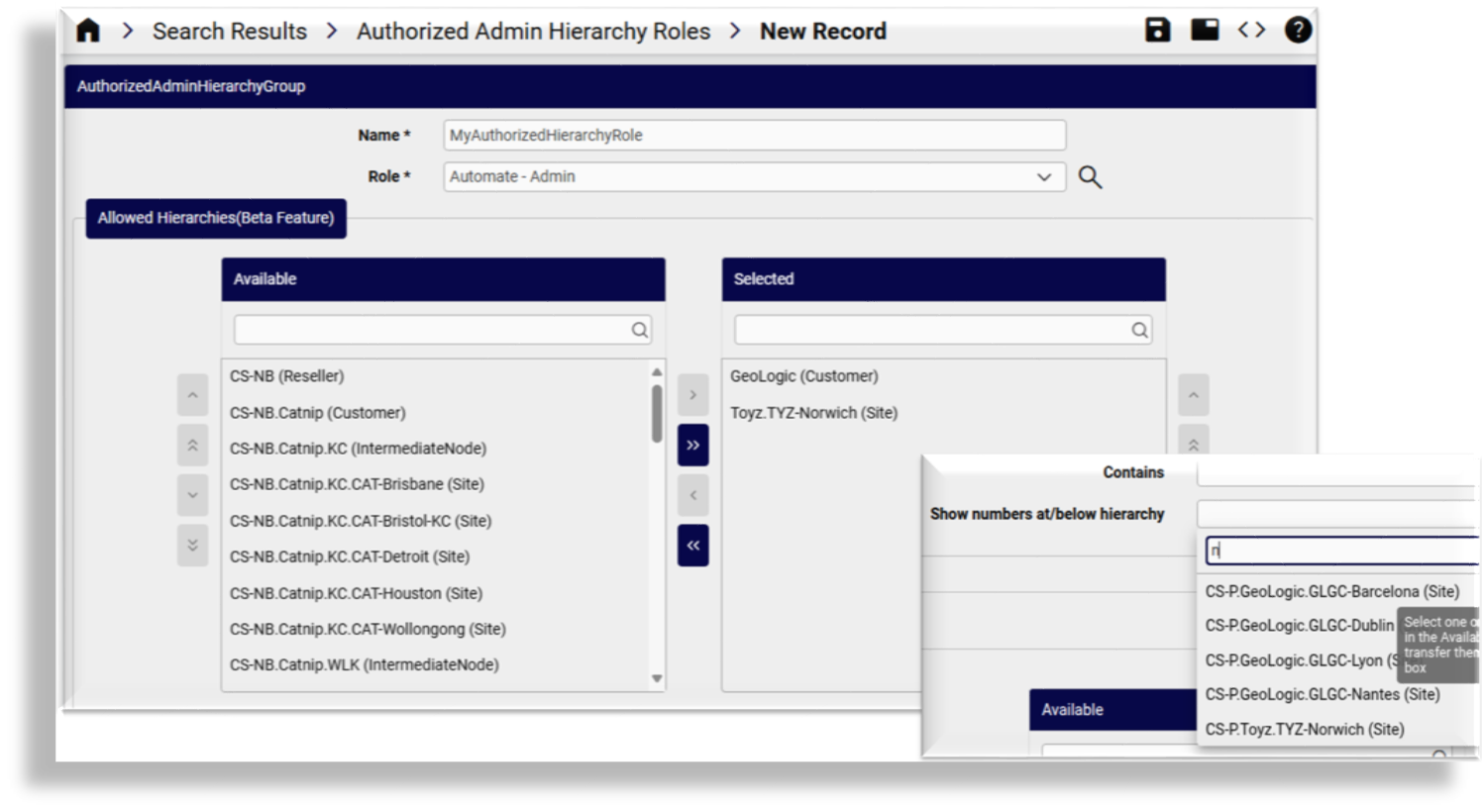
The Available list of the Allowed Hierarchies transfer box (displayed in a shortened format, with type indicator added) shows the items below the hierarchy of the Authorized Admin Hierarchy Roles instance to which the current administrator has access, for example:

Using the side-by-side controls, move the required hierarchies to the Selected list in accordance with your needs, for example, so that they correspond with the administrative domains needed by the administrator that you wish to create. Recall that if a hierarchy is selected, the authorization also applies to any child hierarchy nodes of the selection.
Note
The transfer box in this feature supports a maximum of 500 entries, so that a Selected list can be up to 500 hierarchy entries.
The selection of hierarchies in the transfer box is not mandatory: if no hierarchies are selected, the created authorized admin hierarchy role will have access to the hierarchies as per the role settings and position in the hierarchy structure.
Click Save
This authorized admin hierarchy role can now be assigned to:
an administrator on the Admins page
a user on the User Details page
The created Authorized Admin Hierarchy is available in the drop-down list at the created hierarchy on the form and can then be selected.
Important
If an Authorized Admin Hierarchy is assigned to a user, the allowed hierarchies of this authorized admin hierarchy role override the default Hierarchies Allowed to a user if they were only assigned a role - see: Role Management.
Administrator access to a subset of a hierarchy details#
This section provides further details on and examples of the behaviour of Automate when an administrator has been assigned an Authorized Hierarchy Roles instance.
Hierarchy access illustration#
Consider an administrator added at a customer level hierarchy (Cust2)
where the selected hierarchies of the assigned Authorized Admin Hierarchy (AAH)
are: Site1 and IN1 (Intermediate Node 1) (green nodes in the diagram below).
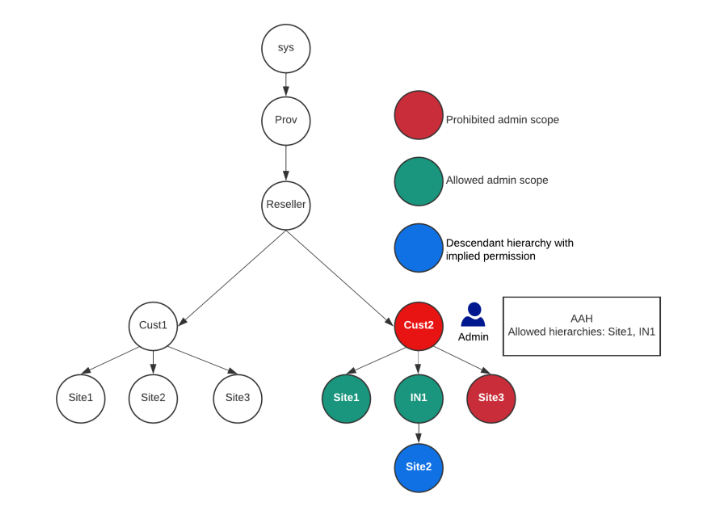
This administrator can only view and manage resources at:
Cust2.Site1Cust2.IN1.Site2, sinceIN1is authorized andIN1.Site2is a child hierarchy.
Authorized Admin Hierarchy and user management#
For an administrator with an authorized admin hierarchy role that also manages
the authorized admin hierarchy role of a user, this management (for example, selection/removal
of hierarchies) is restricted by the allowed hierarchies of the administrator.
In other words, an administrator can only add/modify data/AuthorizedAdminHierarchy instances
with allowed_hierachies that are set to those hierarchies that the administrator has access to.
For user management, a site administrator cannot for example carry out updates on a user who has administrator access to both the parent customer hierarchy and who also has self-service user access to the same site.
For example, an administrator with access to a limited subset of hierarchies can only change the password of another user on condition that the administrator has access to all the hierarchies that the other user has access to. This prevents privilege escalation by password change.
Authorized Admin Hierarchy Roles display on the user interface#
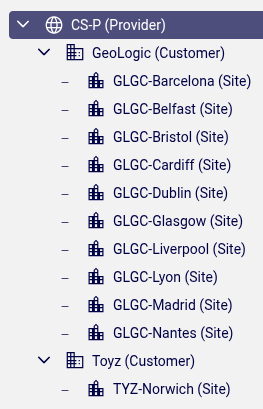
Below are a number of examples on the user interface that reflect the display seen by an administrator with an authorized admin hierarchy role that contains the following selected hierarchies in a hierarchy tree:
a customer hierarchy node:
Geologic (Customer)a single site hierarchy node below a customer
Toyz (Customer)calledTYZ-Norwich (Site)
Hierarchy tree
Note that the displayed tree reflects nodes that are not selected hierarchies:
Toyz (Customer) and CS-P (Provider). These nodes are included in the tree view
in order to show the hierarchy context for the selected hierarchies.
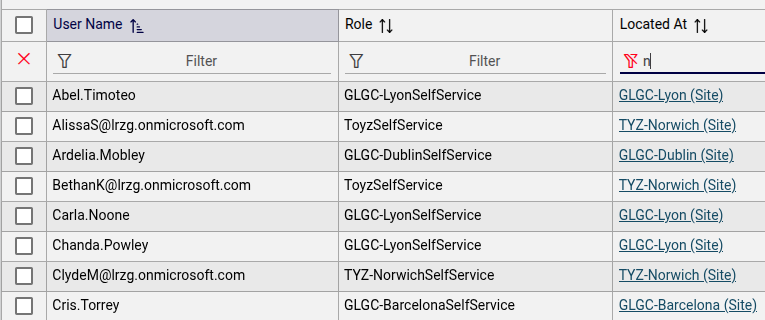
List view (users)
A user list only shows users located at hierarchy nodes matching the authorized admin hierarchy role associated with the administrator.
Filtered lists
Authorized hierarchy filtered drop-down lists include:
List of users on the Quick User form
Hierarchy choices when Quick User is triggered while at non-site hierarchy
Network Device Selection pop-ups
Hierarchy choices in Internal Number Inventory forms
Example of filtering during number management:
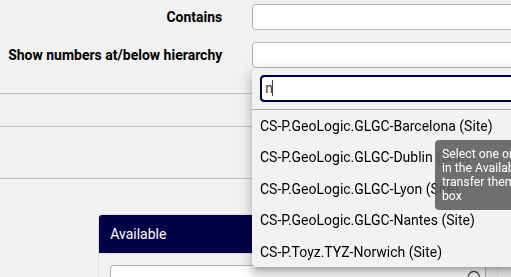
Overbuild#
The administrator must have permissions to the customer “From” hierarchy, which implies access to all sites under the customer.
On the default dashboard and menu items providing
access to the Overbuild feature a macro condition at the customer hierarchy needs to evaluate to true
before the items are accessible:
(( fn.authorized_admin_allowed_hierarchy_level Customer == fn.true ))
Microsoft License Allocation#
Where Microsoft 365 user licenses are available to an organization as a whole on a single Microsoft tenant and Automate is used to support for the allocation of these licenses to various business units and departments within such an organization represented as hierarchies in Automate, the number of un-allocated licenses shown as Maximum Limit Allowed on Microsoft License Allocation will however show total values that include hierarchies excluded from the administrator’s allowed hierarchies.
This complete total is shown to ensure that such an administrator has an accurate view of available licenses for allocation.
For details on this feature, see Microsoft license management and alerting in the Core Feature Guide.
Authorized Admin Hierarchy Roles and number management#
Number range management is only available for specific authorized admin hierarchy roles: if the authorized admin hierarchy role associated with an administrator does not include customer-level hierarchies, it is not available, since the Automate API only allows for the creation of a number inventory at the customer hierarchy.
As an example of number range visibility by hierarchy, consider an administrator with authorized admin hierarchy roles access to intermediate level A and thus has access to all the sites under this level. In addition the administrator has access to only one or two sites from intermediate level B. In accordance with the site the administrator is at, the visibility of numbers will be from that site level upwards in the hierarchy. The intermediate level A numbers will thus not be visible if the administrator is at a site under intermediate level B.
See: Number range management.
Authorized Admin Hierarchy Roles on the system API#
Tasks and activities involving the system API are also in accordance with the authorized admin hierarchy role associated with the administrator.
This can for example be seen when using the Macro Evaluator
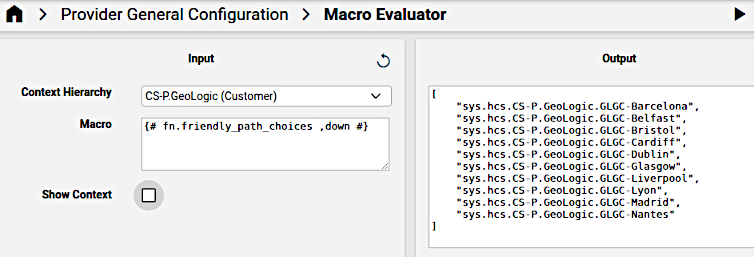
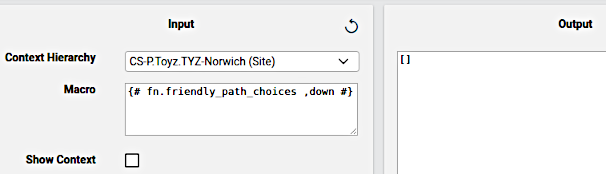
Macros and macro functions are integrated into API related system workflows and elements such as configuration templates and GUI rules.
Similarly, a Bulk Load JSON file or MS Excel sheet load transaction containing an update request for a user outside of the authorized admin hierarchy role associated with the administrator will yield an appropriate error:
The current request user does not have sufficient
allowed hierarchy access to modify a
user with Authorized Admin Hierarchy set to ...
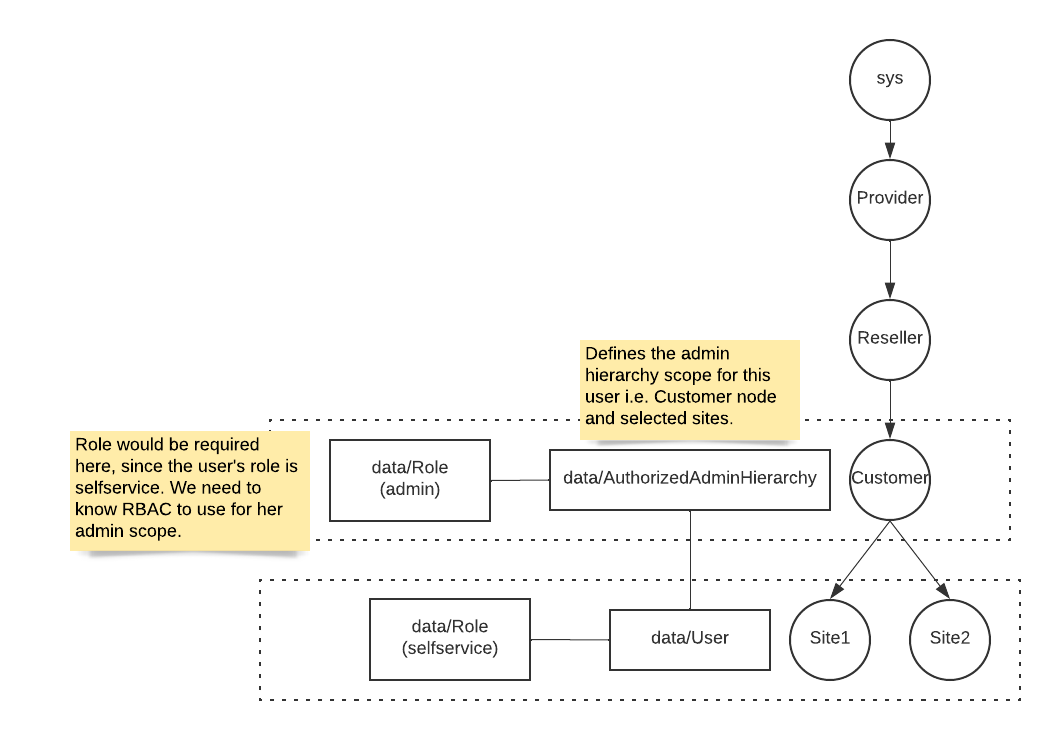
End User and Administrator details#
Provision the end user as usual.
Associate the end user with an Authorized Admin Hierarchy Roles instance.
An authorized admin hierarchy roles instance contains a role. This instance can then be assigned to a user so that if the user is then also assigned a self-service role, the user is then an end user with admin access: a user with multiple user roles - both a self-service role and this role from the Authorized Admin Hierarchy Roles instance. See: Introduction to role-based access control.
Important
When an Authorized Admin Hierarchy is set for a user, the hierarchy of that instance (the model
data/AuthorizedAdminHierarchyinstance) as well as its descendants will be visible as authorized hierarchies for administration purposes.An administrator who is also a self-service user, cannot update own user settings control level (e.g. hierarchy access) - only provisioned elements for the user (number, license, etc.) can be updated.
Users with multiple user roles then have a User Type of “End User + Admin”. See: Add admin user.
Upon user login, the Automate system then assigns the appropriate role to the user in accordance with the requested portal:
Portal |
Role |
|---|---|
Automate Self-service |
selfservice |
Automate Admin |
administration |
Note
A user with multiple roles can also access both self-service and admin portals during one login session, but a logout on any portal would end the login session on both portals.
For multi-role admin user SSO login options, see: SSO Scenarios for Multi User Roles under Configure Self-service SSO SP settings.
When multi-role users perform administrative actions, they can manage their own services such as adding new Phones and Lines. However, the administrators would not be able to make modifications that altered their own role-based access configuration, such as change of role and associated Authorized Admin Hierarchy.
Related Topics
For API details, see the
API Request Headers.REQUEST-PORTALAPI request header in:
