Introduction to role-based access control#
Overview#
Automate ships with a streamlined, role-based access control (RBAC) system to manage what users can see and do across different hierarchy levels. Roles directly determine a user’s interface experience, permissions, and access scope, ensuring secure and tailored access to system resources.
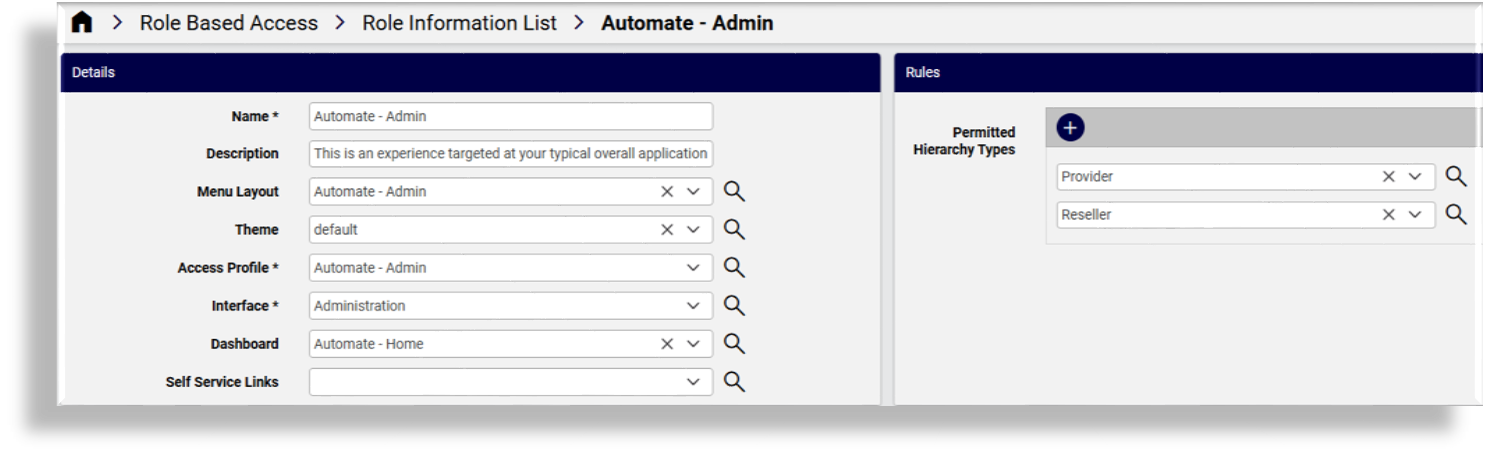
A user’s role defines their experience and access by combining the following components:
Component |
Description |
|---|---|
Dashboard |
The landing page shown after login, including widgets and links. |
Menu Layout |
Defines the navigation menu and associated configuration templates and field display policies (FDPs). |
Theme |
Controls the visual appearance of the interface. |
Access Profile |
Specifies permissions for accessing and managing system resources. |
Interface |
Indicates whether the role applies to the Administration or Self-service interface. |
These components are managed via the data/Role model and are visible in the Role Management
list view.
Related topics
Default experience-based roles#
Automate ships with ready-to-use roles that reflect common user experiences:
Automate - Admin
Automate - Admin - Microsoft Only
Automate - License Manager
Automate - Self Service
Automate - Service Desk
Automate - Service Desk - Microsoft Only
Automate - Analyst
HcsAdmin
Each shipped role includes a predefined dashboard, menu layout, theme, and access profile. These roles reside at hcs level and don’t require cloning as they can
be assigned directly. However, the hcsadmin user can clone and customize them if needed.
Note
Users cannot modify their own role or its associated dashboard, menu layout, access profile, configuration templates, or field display policies.
Related topics
Role assignment#
When creating or updating a user, you can assign them a role from the available list. The assigned role determines:
What the user sees upon login
Which menus and actions are available
What permissions they have
The interface styling and layout
Roles can be reused across multiple users and assigned at any hierarchy level, provided the role supports that level.
Custom roles#
You can create custom roles by defining your own combinations of dashboard, menu layout, theme, and
access profile, or the hcsadmin user can clone and customize one of the predefined roles that ship with the system.
All roles are managed entirely through the data/Role model.
Note
You cannot edit your own role.
Related topics
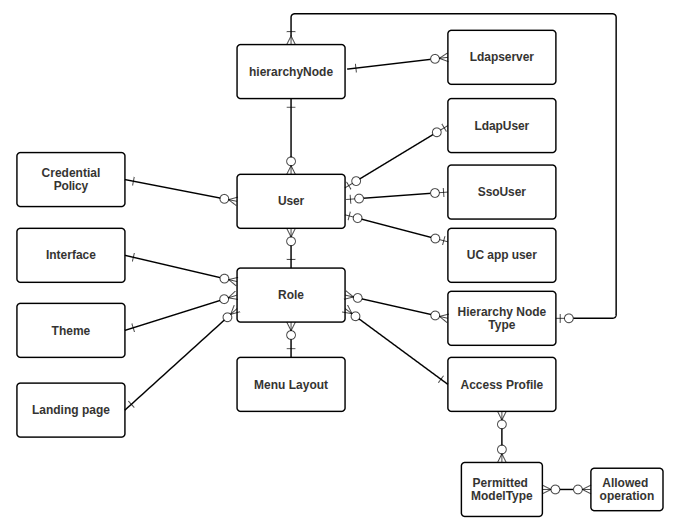
Hierarchy awareness#
Role-based access control is implemented through:
Hierarchies and user roles
Authorized Admin Hierarchies, Authorized Admin Hierarchy roles, and roles
Users are created at a specific hierarchy level. They can view and manage resources only within their assigned level and below. Some roles are restricted to certain levels based on predefined hierarchy rules. For example, a site admin role may only be assigned to users at the site level.
Authorized Admin Hierarchy roles allow more flexible access configurations, where roles can be selected and added to an Authorized Admin Hierarchy.
Each role includes:
Hierarchy rules: Roles are only available at permitted hierarchy types defined for the role.
Allowed hierarchies: Hierarchies selected from a list and applied to the role.
System permissions: Access to resources and operations within the hierarchy.
Access profiles: Define operations and permissions.
Interface customization: Includes visibility of resource attributes, default values, and UI appearance.
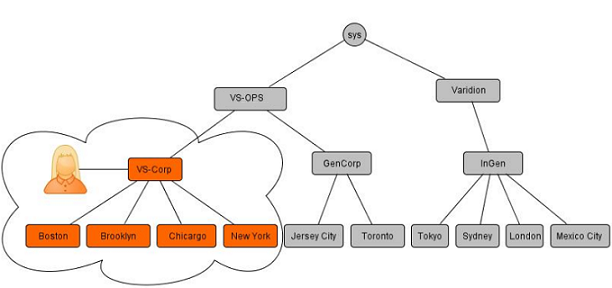
The image provides an example of the following scenario:
A user at VS-Corp cannot view resources in GenCorp or InGen
Users can navigate down the hierarchy tree but not across or above their assigned level.
This ensures that users only access data relevant to their organizational scope.
Related topics
