Controls#
Overview#
The Controls configuration panel allows you to define a script or routine that can be executed by a response procedure or attached as a probe. These controls can be passed variables extracted from a correlation rule. The resulting return of the scripts execution can be mapped to the database, used as an action or can be injected back into the system to be correlated against another element.
Add or delete a control#
To add a new control or delete an existing control:
Log in to Arbitrator, then click the toolbar Wrench icon to launch Arbitrator’s System Configuration GUI.
Select the Controls icon to open the Controls configuration panel.
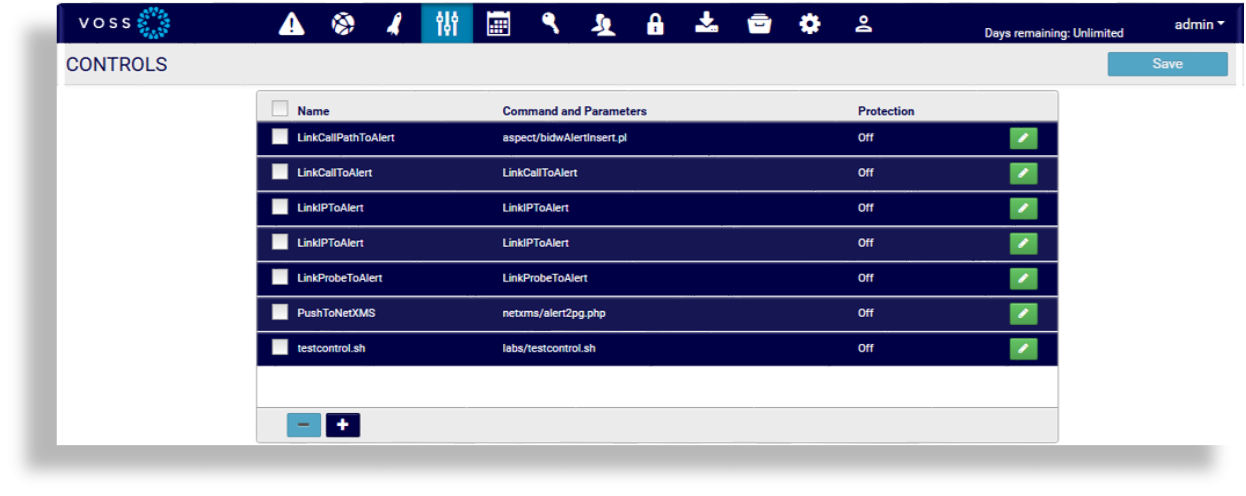
Are you adding a new control or deleting an existing control?
Adding a new control. Click the Plus icon to add a new control. Go to the next step.
Deleting an existing control. Select the checkbox adjacent to the control name; then, click the Minus icon at the bottom of the panel. The control is removed.
Fill out a name for the new control.
Is this a system or custom control?
Custom control. Select the Custom checkbox. Fill out a command and parameters (the script to execute).
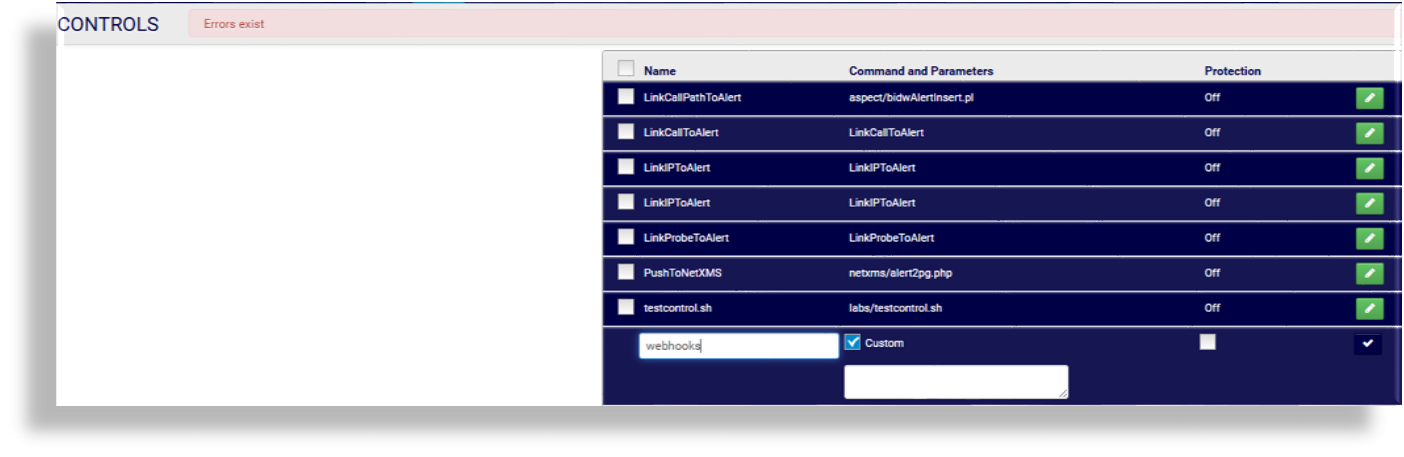
System control. Clear the Custom checkbox. From Select Category, select a control category to populate the Select Script drop-down, then select a script, and fill out any additional information required for the selected script (additional fields may display).
When you’re done, select the checkmark icon to add your changes, then click Save to add the new control.
Send alerts to a 3rd party system using a webhook#
This procedure adds a control to send JSON format alerts to a 3rd party system using a webhook.
Note
This control specifies a script to push alert information via a curl command (POST) that includes the URL of the system that will receive the alert.
In Arbitrator, add a control for the alert. See Add or delete a control.
Add a name for the alert.
Ensure the Custom checkbox is selected.
In the Command and Parameters field, fill out the script name,
webhooks/alert_webhooks.php, then fill out the URL of the 3rd party system, for example,webhooks/alert_webhooks.php https://10.45.0.55/log/events/webhooks.Note
When an alert is generated, the destination specified by this URL must be able to receive the alert data from Arbitrator via a curl POST.
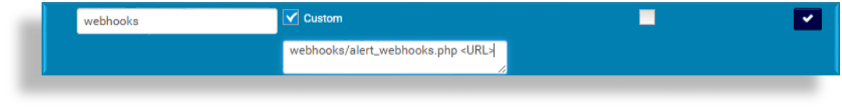
Click the checkmark to the right of the fields you’re working with to mark your configuration as done, then click Save to add the control.
Assign the control to a response procedure. See Response Procedure Configuration.
In Arbitrator, go to Response Procedure Configuration.
Create the webhook response procedure and select it.
In the Response Procedure Details pane, select Alert.
Click + Control to assign the webhook to the alert control.
Add credentials for the receiver (the destination specified in the URL for the control).
Assign the alert control to a policy. See Policy Configuration.
What happens when an alert is triggered?
When a policy associated with the webhook alert is triggered, it triggers the webhook alert. The alert is sent to the receiving system as a POST. The destination system receives a JSON format alert message.
The alert payload message includes the following details:
Status code
The policy
The rule
The reference ID
A timestamp

