Configure Insights integration with CUBE#
Overview#
This procedure configures Insights Arbitrator integration with Cisco Unified Border Element (CUBE) for call detail record (CDR) ingestion and monitoring.
Once the CUBE is configured to send CDRs to the Arbitrator, CDR files are placed in the relevant directory (the folder name is the IP address of the CUBE), triggering the Arbitrator to parse the CDRs files so that the data will be available on the CUBE dashboard.
Note
If you wish to monitor Cisco CUBE SRST/ISR status and display this data in the CUBE dashboard with an ssh probe over SNMP probe, run the following command:
show voice dial-peer status
Queries syslog message for registered/unregistered to show voice registar pool
Queries the server via syslog and returns a list of all registered MAC addresses
This procedure involves two steps:
Related topics
Add the CUBE via the Arbitrator CLI#
This procedure sets up the CUBE on the Arbitrator.
Log in to the Arbitrator CLI as admin.
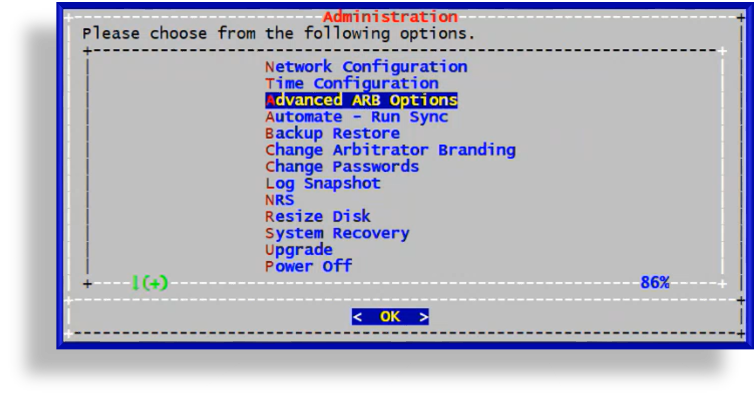
On the Administration menu, select Advanced ARB Options.
In the Main Menu, press
3to choose option 3, Advanced.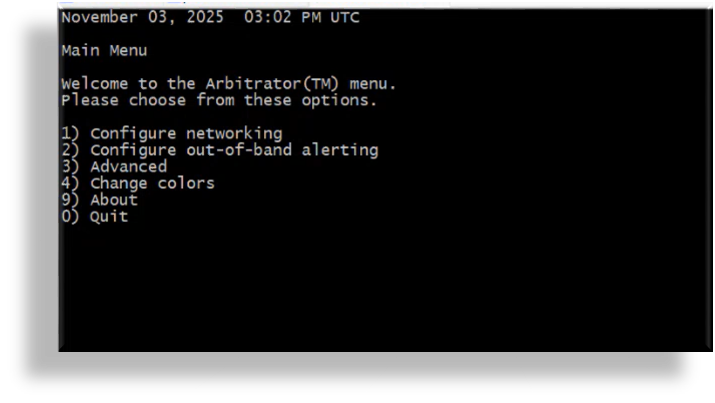
In the Network Menu, press
3to choose option 3, Configure services.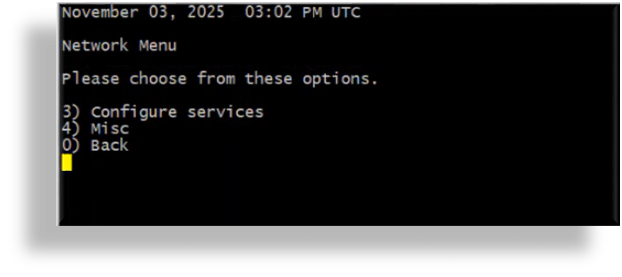
In the Services Menu, press
4to choose option 4, Cisco Services.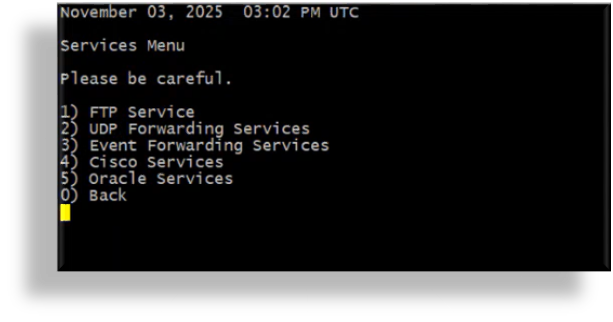
In the Cisco Services Menu, press
3to choose option 3, Configure Cisco Unified Border Element (CUBE).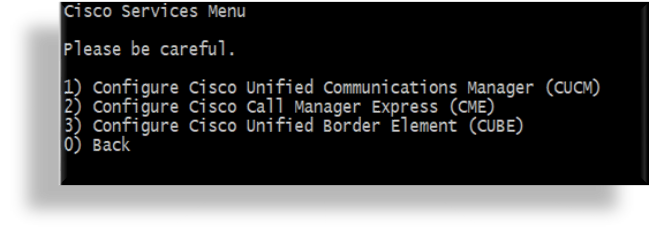
In the Cisco CUBE Menu, you can view, add, or delete Cisco CUBEs, or clear all Cisco CUBE configuration. In this case, to add a Cisco CUBE, press
2to choose option 2, Add Cisco CUBE.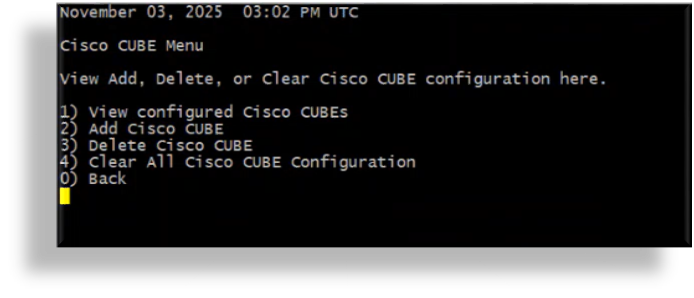
Fill out the IP address of your CUBE to add its IP address to a folder on the Arbitrator. Press keyboard shortcut Ctrl-X.
The CUBE’s IP address is added to the following location on the Arbitrator:
/chroot/scp/pub/cube/<IP address of your cube>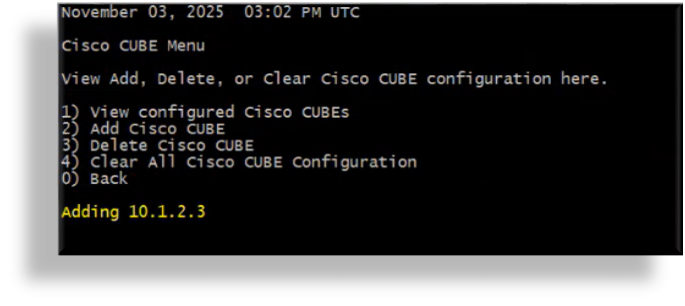
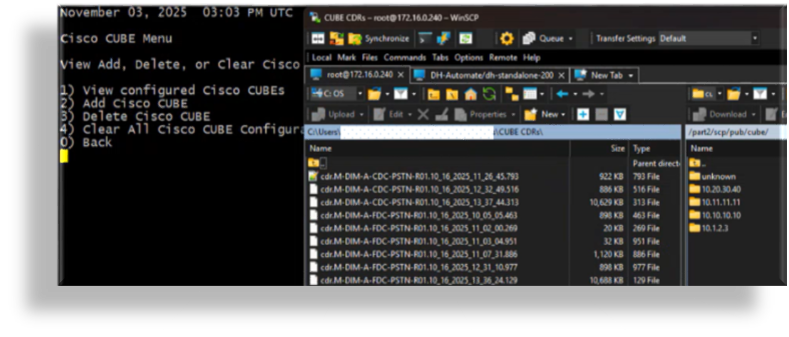
Once CDRs are placed in the directory created for the CUBE, Arbitrator parses the files and the data will be available on the CUBE dashboard.
Next steps
Related topics
Configure the CUBE to send CDRs to the Arbitrator#
This procedure configures the queue on a CUBE to send detailed CDRs to Arbitrator via SFTP to a specified server under given user credentials, with files flushed every one second, and using “primary sftp” keyword to set the SFTP destination.
Note
Once the setup and configuration is complete, you can monitor CDR file creation and transmission status
on CUBE via show commands or logs.
The configuration typically involves:
Enabling file accounting on CUBE.
Specifying the SFTP server details, including IP/hostname, username, password, and directory path. Credentials and directory path depend on your SFTP server (Arbitrator) setup. The drop account username is “drop”. You can set the drop account password via the Administration menu. See Creating and managing SFTP users in the Insights Security Guide.
Setting retry and file retention options as required. The flush parameter can be configured as needed. In this procedure we’re configuring a maximum flush every second (parameter value of 1).
Pre-requisites
Ensure port 22 is open outbound from the CUBE to the SFTP server. Typically, only FTP on port 21 is available.
Cisco CUBE version 14.6 and up.
Note
Cisco CUBE version 14.6 and up support sending CDR files directly to an SFTP server. SFTP might not be supported directly for CUBE versions earlier than 14.6.
Configure CDR file accounting on CUBE with SFTP
Perform this series of basic commands on CUBE:
text
enable
configure terminal
aw-accounting file
cdr-format detailed
primary sftp <SFTP-server-IP-or-hostname>/path_ username <username> password <password>
maximum cdrflush-timer 1
end
write
The table provides additional details for the parameters in the commands used to configure the CUBE, for example, in the following:
primary sftp 172.16.0.240/cube/110.1.1.1 usr: drop pass: droppassword
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
The primary address, which sets the SFTP destination. In the example,
|
|
The IP address of the CUBE. In the example, this is |
|
Your drop password. |
|
Configurable retry and retention value, set to one (1) second in the example, which does a maximum flush every second. |
Related topics
