Introduction to PSTN Call Processing and Routing¶
PSTN call processing and routing leverages two VOSS-4-UC 10.x/11.5(x) features:
- Calling Search Space (CSS) hierarchy
- Name Local Route Group
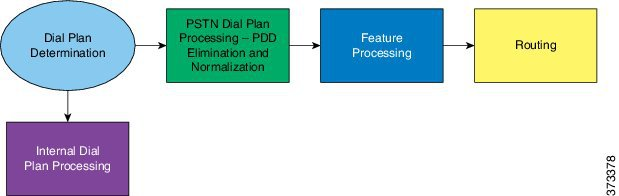
Call processing includes the following stages:
- Dial plan determination (internal and PSTN dial plan)
- Country dial Plan post-dialing delay (PDD) elimination, normalization, and call type classification (applies to PSTN calling only)
- Feature processing - Forced On-Net, Origination Call Screening, Time of Day, Calling Line Identification Restriction (CLIR), Calling Line Identification Presentation (CLIP), Forced Authorization Code and CMC (applies to PSTN calling only)
- Line or device based routing
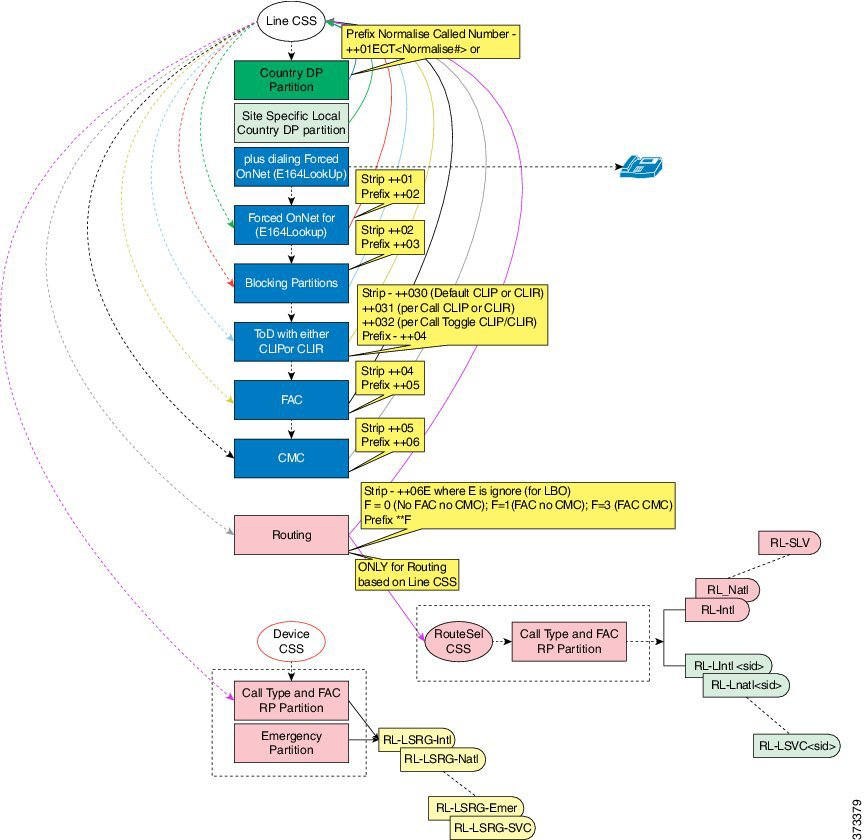
Figure 1. Call Processing Stages
One change from CUCDM 8.1(x) is that features and routing are based on call type rather than dialed number. The biggest advantage of using call type classification is that most features are independent of the country dial plan. Adding a country dial plan defines the dialing behavior patterns, classifying them into different call types, and defining routing.
There are two caveats on using feature chaining and call type classification:
- In order to bypass a feature within a feature, a nil feature is implemented.
- For some features (for example FONet), call type classification must be de-classified and reclassified to handle the feature.
Figure 2. Call Processing Implementation