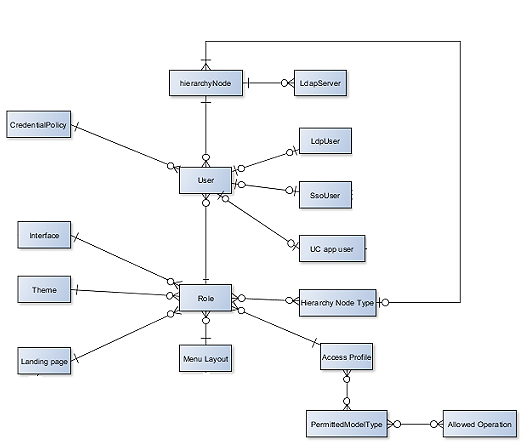
Role Based Access¶
The system implements role-based access control by means of the following components:
- Hierarchy
- User Role
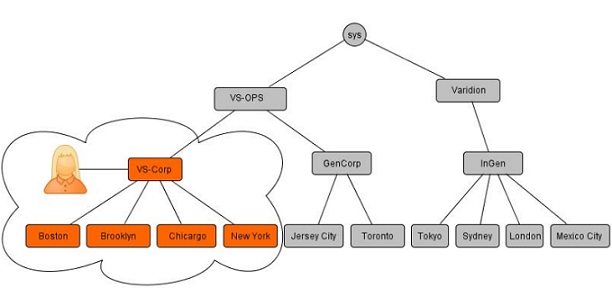
All users that are added to the the system are added at a hierarchy level. Such a user then only has visibility of, and access to, system resources that are available to users at that hierarchy level.
On the interface, this means that the user has no visibility of nodes outside of the sub-tree starting at the parent hierarchy. The user may change to a level of the hierarchy below the the parent hierarchy.
The following diagram shows that a user at VS-Corp has no visibility of GenCorp and InGen.
From the context of the hierarchy level that a user was created at, role-based access is implemented. When users are added to the system at a hierarchy level, a User Role can be assigned to them.
The User Role is a combination of:
- The rules that apply to the role. In particular, the hierarchy types that apply to the role. This means that the role is only available to a user at a hierarchy level that belongs to a hierarchy type associated with the role. For example, a Site Administrator role may have a rule that associates it with Site and Building hierarchy types, but not Customer hierarchy types. In this way a Site Administrator role cannot be associated with a user created at a Customer hierarchy level. A hierarchy rule is therefore enforced by the role.
- System permissions to resources from that hierarchy.
- Access Profiles associated with a User Role that determine access specific operations supported by different models and/or on miscellaneous permissions.
- The visibility of resource attributes.
- The look and feel of the interface.
- Default values of resource attributes.